|
Dew Math for .NET
|
|
Dew Math for .NET
|
Minimizes the function of several variables by using the Conjugate gradient optimization algorithm.
|
Parameters |
Description |
|
TRealFunction Fun |
Real function (must be of TRealFunction type) to be minimized. |
|
TGrad Grad |
The gradient and Hessian procedure (must be of TGrad type), used for calculating the gradient. |
|
ref double[] Pars |
Stores the initial estimates for parameters (minimum estimate). After the call to routine returns adjusted calculated values (minimum position). |
|
[In] double[] Consts |
Additional Fun constant parameteres (can be/is usually nil). |
|
[In] object[] ObjConst |
Additional Fun constant parameteres (can be/is usually nil). |
|
out double FMin |
Returns function value at minimum. |
|
out TOptStopReason StopReason |
Returns reason why minimum search stopped (see TOptStopReason). |
|
[In] TMtxFloatPrecision FloatPrecision |
Specifies the floating point precision to be used by the routine. |
|
bool FletcherAlgo |
If True, ConjGrad procedure will use Fletcher-Reeves method. If false, ConjGrad procedure will use Polak-Ribiere method. |
|
bool SoftLineSearch |
If True, ConjGrad internal line search algoritm will use soft line search method. Set SoftLineSearch to true if you're using numerical approximation for gradient. If SoftLineSearch if false, ConjGrad internal line search algorithm will use exact line search method. Set SoftLineSearch to false if you're using *exact* gradient. |
|
int MaxIter |
Maximum allowed numer of minimum search iterations. |
|
double Tol |
Desired Pars - minimum position tolerance. |
|
double GradTol |
Minimum allowed gradient C-Norm. |
|
[In] TStrings Verbose |
If assigned, stores Fun, evaluated at each iteration step. Optionally, you can also pass TOptControl object to the Verbose parameter. This allows the optimization procedure to be interrupted from another thread and optionally also allows logging and iteration count monitoring. |
the number of iterations required to reach the solution(minimum) within given tolerance.
Problem: Find the minimum of the "Banana" function by using the Conjugate gradient method.
Solution:The Banana function is defined by the following equation:
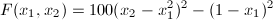
Normally ConjGrad method would also require gradient procedure. But in this example we'll use the numerical approximation, more precisely the MtxIntDiff.NumericGradRichardson routine. This is done by specifying NumericGradRichardson routine as Grad parameter in ConjGrad routine call (see below)
|
Copyright (c) 1999-2024 by Dew Research. All rights reserved.
|
|
What do you think about this topic? Send feedback!
|